Often the building site has a tricky terrain, and to plan it for convenient operation, you need to build a couple or three retaining walls. What is it - a retaining wall, and how to perform it competently so that it does not collapse from the pressure of the soil, and the site with a slope turned into flat terraces? In this article, we will understand the principles of design of retaining walls, consider what loads on them, and intelligently approach the retaining wall's calculation and design.

The retaining wall on the site is most often a monolithic cantilever wall that creates a height difference. In what cases is it needed? For example, the entrance to the garage that is in the basement. The walls enclosing this entrance are retaining walls. Often you still have to make a retaining wall fence when your lot is above or below the surrounding area.
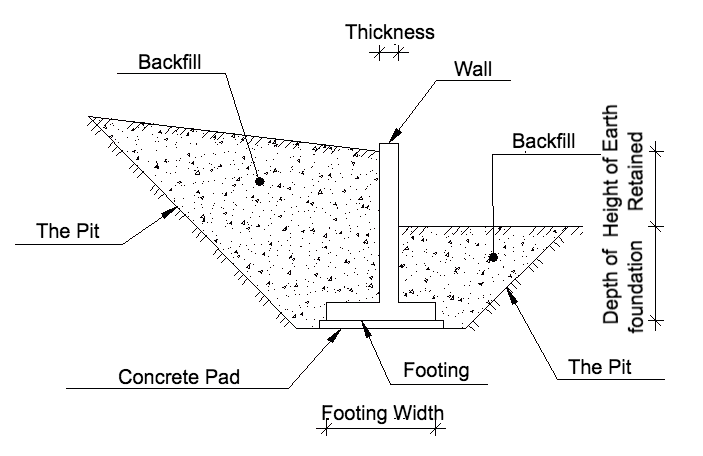
What are the design features of a retaining wall? In addition to the vertical wall, it necessarily has a footing. Let's consider why this important structural detail is needed. As we can see in the figure, the pressure of the ground acts on the wall. Moreover, on the high side, the sheer force acts on the wall, and on the low side, the restraining force acts on the wall. Naturally, the sheer force is always greater than the restraining force - that's the essence of retaining walls. Ground pressure is a serious thing; you can't joke with it. How often in terrain slopes slide down, it's all due to ground pressure. To resist this constant force, you need to design a retaining wall so that it resists shear.
Let's imagine a wall without a footing. What will happen to it? It will simply tilt under the action of the soil, and the greater the difference in levels of the ground, the greater the likelihood of tilt and destruction of the wall. So what does the footing do? It serves as a kind of anchor and holds the wall structure in a stable position: the wider the footing, the more stable the position of the retaining wall.
Let's understand how it works. So, we already know that a shear force is acting against us. What can we counter it with?
1) It's a restraining force on the backside of the backfill. It is, of course, much smaller than the shear force, but it must be taken into account in the calculation.
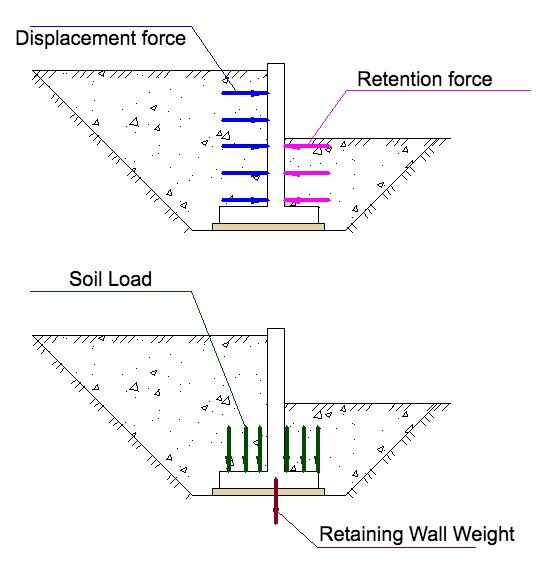
The second factor is the friction force under the footing, which will eventually help us hold the wall in place. The amount of friction force depends on the load, which consists of the retaining wall's own weight and the weight of the soil pressing down on the sole. The wider the footing, the greater the holding friction force.
So, we have understood the forces acting on the retaining wall. Now let's figure out how to approach the design and calculation of the wall.
The first thing we know - is the height difference on the site. From this value and we will start. To take the final height of the retaining wall, we will add to the height of the difference of 50 ... 100 mm at the top so that the soil is not poured, and of course, we will lower the base of the wall to the freezing depth of the soil.
If you do the calculation by hand, it's quite a laborious process, based on the method of selection. You set the base width of the retaining wall and all the overall dimensions, then do a stability test, determine the calculated resistance of the soil under the footing, then, if everything went well, count the reinforcement of the wall and the footing. Nowadays, there are a lot of calculation programs that do all the calculations automatically. If you have such a program, it will save time and effort, and the errors will protect you. If there is no program, you can use the Manual on the design of retaining walls and basement walls and perform the calculation yourself.
One more important point: to make a retaining wall calculation, you must have the results of the engineering-geological survey as the results of the calculation depend very much on the soil characteristics of the construction site.



