Concrete floor slab construction process includes erection of formwork, placement of reinforcement, pouring, compacting and finishing concrete and lastly removal of formwork and curing of concrete slab.
Assemble and Erect Formwork
Prepare and Place Reinforcement
Pour, Compact and Finish Concrete
Curing Concrete and Remove Formwork
1. Assemble and Erect Formwork for Slab
The formwork shall be designed to withstand construction loads such as fresh concrete pressure and weight of workers and operators and their machines.
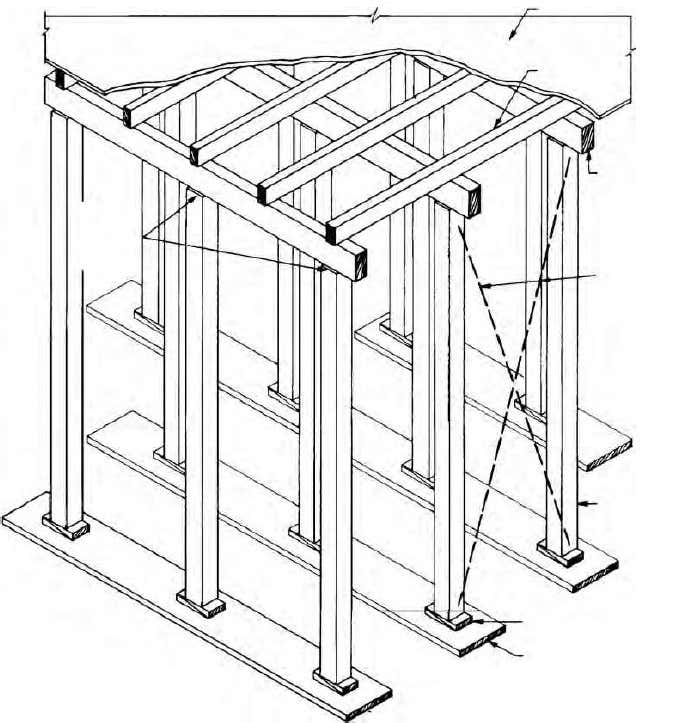
Moreover, there are various construction aspects that need to be considered during the erection of formworks. For example, it should be positioned correctly, lined and levelled, joints sealed adequately, and prevent protruding of nails into the concrete etc…
Furthermore, different materials such as wood, steel, and aluminum can be used for the formworks of concrete floor slab.
Finally, there are several common formwork construction deficiencies that site engineer needs to be aware of and prevent their occurrence otherwise formwork failure may occur. These construction deficiencies are provided below:
- Poor or lack of formwork examination during and after concrete placement to identify uncommon deflections or other indications of possible failure that could be corrected
- Inadequate nailing, bolting, welding, or fastening
- Improper lateral bracing
- Construct formwork that does not comply with form drawings
- Lack of proper field inspection to ensure that form design has been properly interpreted by form builders
- Use of damaged or inferior lumber having lower strength than needed.
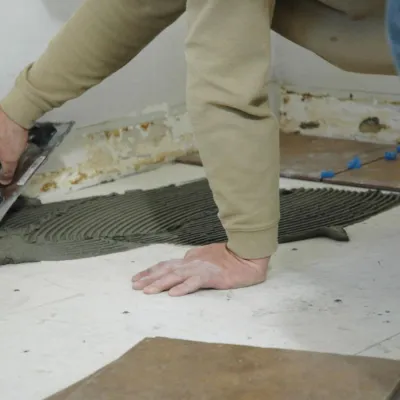
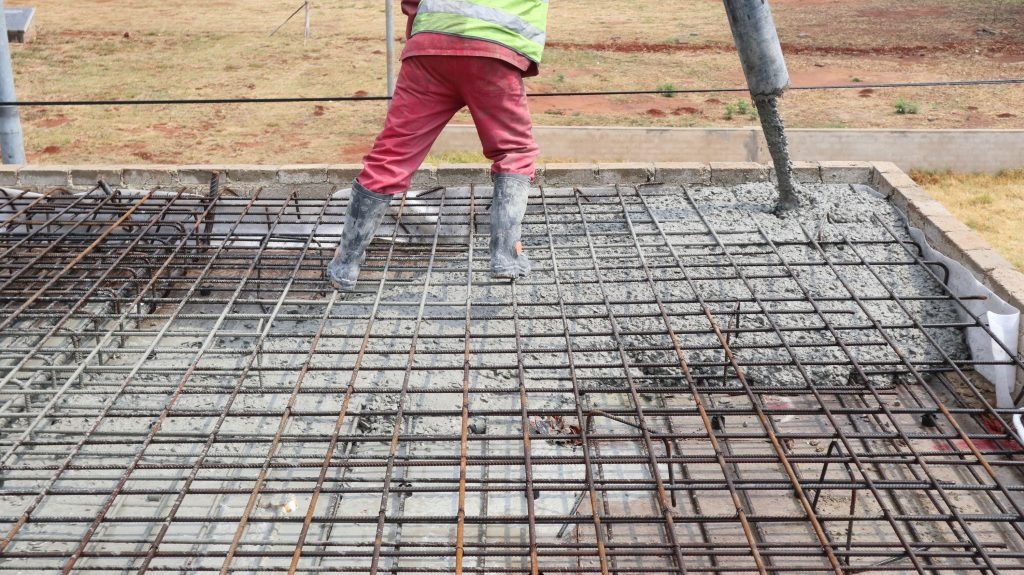
2. Prepare and Place Reinforcement for Slab
Prior to the placement of reinforcement for concrete floor slab construction, inspect and check forms to confirm that the dimensions and the location of the concrete members conform to the structural plans.
Added to that, the forms shall be properly cleaned and oiled but not in such amount as to run onto bars or concrete construction joints.
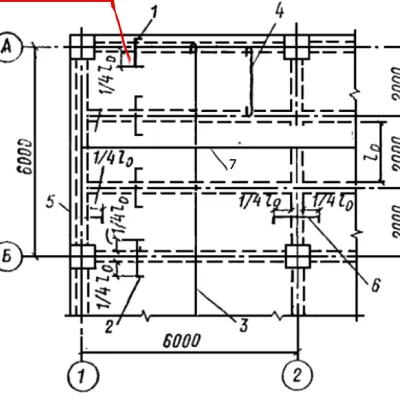
Design drawings provides necessary reinforcement details, so it only needs understanding to use designated bar size, cutting required length, and make necessary hooks and bents.
After preparation is completed, steel rebars are placed into their positions with the provision of specified spacings and concrete cover.
The concrete cover and spacing for floor slabs can be maintained by introducing spacers and rebars supporters. Wires are used to tie main reinforcement and shrinkage and temperature reinforcement (distribution reinforcement).
It should be known that incorrect reinforcing steel placement can lead to serious concrete structural failures. Improper concrete cover exposes reinforcement bars to danger and jeopardize concrete-steel bond.
Finally, after all requirements of reinforcement placements (positions, concrete cover, spacing, and correct rebars size; length; hooks; and bending) are finalized, then site engineer can order concreting.
3. Pour, Compact and Finishing Concrete Floor Slab
Mixing, transporting, and handling of concrete shall be properly coordinated with placing and finishing works. In floor slab, begin concrete placing along the perimeter at one end of the work with each batch placed against previously dispatched concrete.

Concrete should be deposited at, or as close as possible to, its final position in order to prevent segregation. So, Concrete placement in large and separate piles, then moving them horizontally into final position shall be prevented.
Moreover, site engineer shall monitor concreting properly, and look for signs of problems. For example, loss of grout is the indication of improper sealing and movement of joints. Added to that, cracking, excessive deflection, level and plumb, and any movement shall be checked and tackled to prevent further problems.
Furthermore, fresh concrete should be compacted adequately in order to mold it within the forms and around embedded items and reinforcement and to eliminate stone pockets, honeycomb, and entrapped air. The duration of vibration at each position should ensure sufficient compaction of the concrete mixture, the main signs of which are the cessation of its subsidence, the appearance of cement milk on the surface and the cessation of air bubble emission. Vibration, either internal or external, is the most widely used method for consolidating concrete.
Lastly, slabs could be finished in many ways based on floor application.
4. Curing Concrete and Remove Formwork
After finishing ended, suitable technique shall be used to cure the concrete adequately. Slab curing methods such as water cure; concrete is flooded; ponded; or mist sprayed.
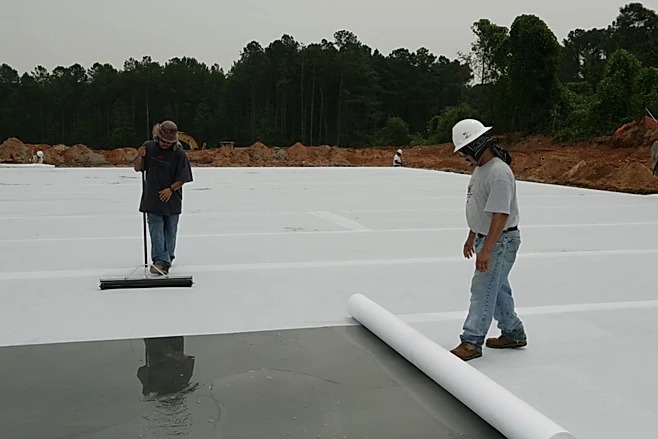

Concrete care must ensure that the proper curing temperature is maintained and that freshly laid concrete is protected from rapid drying. Freshly paved concrete is first of all covered from the effects of rain and sunlight (coverings such as sand; canvas; burlap; or straw) and systematically watered in dry weather for 7 days of concretes on Portland cement or alumina cement and 14 days on other cements (one-time watering 0.5 ... 1.0 kg/m2). In addition to water retaining method used to kept slab surface wet continuously, chemical Membranes,and waterproof paper or plastic film seal. At air temperatures below 5 ° C watering is not carried out. The movement of people on the concreted structures and the installation of scaffolding and formwork on them for the erection of overlying structures is allowed only after the concrete reaches a strength of at least 1.2 MPa.